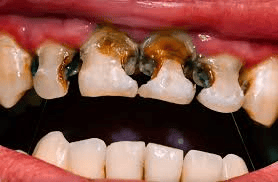
Identifying the visual characteristics of rotten teeth:
If you’ve ever wondered about the appearance of rotten teeth, it’s crucial to know what signs to look for and what they mean regarding dental health. Rotten teeth, also known as decayed or cavity-ridden teeth, can manifest in several distinct ways. Recognizing the visual characteristics of rotten teeth can lead you to seek timely dental care, which is vital in preventing more severe oral issues.
The first noticeable sign of rotten teeth is discoloration. Healthy teeth are typically bright and white, but a rotten tooth often appears yellow, brown, or even black. This discoloration occurs as the enamel—the outer protective layer—breaks down due to decay. If you notice any shade changes in your teeth, it’s a red flag indicating potential rot beneath the surface.
Another characteristic to look for is the presence of visible holes or pits in the teeth. As decay progresses, it can create cavities, which are small openings in the teeth. You might catch them while brushing or flossing, so it’s a good idea to regularly check your teeth in the mirror. If you see tiny holes, especially in back teeth, it may indicate significant decay.
Additionally, rotten teeth can develop a rough or jagged surface. Healthy teeth typically have smooth edges, but decay can cause the surfaces of the teeth to become uneven. If you run your tongue along the edges of your teeth and feel a roughness or a stark difference in texture, it might be time to consult a dentist.
Another visual sign to consider is swelling or inflammation around the gums. If the area around a rotten tooth looks red, swollen, or bleeds easily, it indicates an underlying problem that usually accompanies tooth decay. Healthy gums are typically light pink and firm, so altered color and texture signal that something is wrong.
Here are some key visual characteristics to remember when identifying rotten teeth:
- Discoloration: Yellow, brown, or black patches.
- Visible Cavities: Small holes or pits.
- Rough Surfaces: Jagged edges or uneven surfaces.
- Gum Issues: Red, swollen, or bleeding gums.
Moreover, you may also notice a persistent bad taste or smell in your mouth, especially when it’s caused by tooth decay. As bacteria build up in the mouth due to rotten teeth, they can produce foul-smelling compounds that lead to halitosis. If you find your breath remains unpleasant despite regular brushing, this might be linked to deeper tooth issues.
It’s essential to heed these signs because the effects of untreated rotten teeth can extend beyond aesthetics. If decay continues without treatment, it can ultimately lead to tooth loss or severe infections. Besides affecting the tooth itself, rotten teeth can also result in pain, difficulty chewing, and even impact speech.
Taking positive action at the first sign of rotten teeth is vital. Make regular dental check-ups a part of your routine to detect problems early. Dentists can provide professional cleaning, fluoride treatments, and other preventive care to help combat tooth decay. Your oral hygiene practices at home cannot be overstated. Daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste and flossing contributes significantly to maintaining tooth health.
Furthermore, be mindful of your diet, as sugary and acidic foods can worsen tooth decay. Limiting these can help keep your smile healthier. It’s also a good habit to stay hydrated and drink water, particularly after consuming meals, to wash away harmful bacteria and food particles.
The causes behind tooth decay and rot:
Tooth decay and rot are significant dental issues that can affect anyone, regardless of age. Understanding the causes behind these problems can help you take better care of your oral health. Several factors contribute to the deterioration of teeth, leading to discomfort and dental treatments. This article will explore these causes in detail.
What causes tooth decay?
Tooth decay occurs when the enamel, the protective outer layer of your teeth, breaks down due to various factors. Here are the primary causes of tooth decay:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on your teeth. This plaque produces acids that erode enamel.
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: Consuming high amounts of sugar feeds the bacteria in your mouth. These bacteria produce more acid, which accelerates tooth decay.
- Acidic Foods and Drinks: Citrus fruits, sodas, and some energy drinks are high in acidity. Regular exposure to these acidic substances can wear down enamel and contribute to decay.
- Dry Mouth: Saliva helps neutralize acids and wash away food particles. A dry mouth, often caused by medications or certain health conditions, can increase the risk of decay.
- Tooth Misalignment: Crooked or overlapping teeth can create hard-to-reach areas for cleaning, leading to plaque buildup and, subsequently, tooth decay.
What leads to tooth rot?
Tooth rot, also known as cavitation, refers to the significant deterioration of tooth structure due to decay. When cavities form, they can lead to holes in the teeth. The following factors can accelerate this process:
- Delayed Treatment: Neglecting a small cavity can result in worsening decay and irreversible damage over time. It’s essential to address dental issues promptly.
- Diet Choices: A diet rich in carbohydrates and sugars significantly contributes to tooth rot. Frequent snacking between meals increases acid attacks on the teeth.
- Not Visiting the Dentist: Regular dental check-ups are essential for monitoring oral health. Dentists can catch early signs of decay before they progress to rot.
- Weak Enamel: Some individuals may have naturally weaker enamel due to genetics or nutritional deficiencies, making their teeth more susceptible to decay and rot.
Additional contributing factors:
In addition to the primary causes, there are other elements that can affect your dental health:
- Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes can increase your risk of tooth decay due to fluctuations in blood sugar levels affecting saliva production.
- Age: As you age, natural wear and tear can weaken your teeth. Older adults may have more difficulty accessing proper dental care.
- Genetics: Your family history may play a role in your susceptibility to dental issues, including enamel thickness and cavity formation.
Preventive measures:
Prevention is key to avoiding tooth decay and rot. Here are some effective strategies:
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Limit Sugary Snacks: Try to reduce your intake of sugary foods and beverages. Opt for healthier snacks like fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
- Visit Your Dentist Regularly: Schedule regular check-ups to ensure your teeth are healthy and catch any potential problems early.
- Use Fluoride: Fluoride helps strengthen enamel. Use fluoride toothpaste and consider fluoride treatments from your dentist.
By understanding the causes behind tooth decay and rot, you can take steps to protect your smile. Prioritizing oral hygiene, making healthy dietary choices, and regularly visiting your dentist are crucial for maintaining your dental health. Make sure to be proactive to ensure the longevity of your teeth and avoid the discomfort of decay and rot.
The impact of rotten teeth on overall health:
Rotten teeth may seem like just a dental concern, but they can have significant effects on your overall health. Understanding how decayed teeth impact your body is crucial for maintaining both dental and general well-being. When teeth begin to rot, they can cause pain, discomfort, and even serious health complications. Here’s what you need to know about this pressing issue.
Common signs of rotten teeth:
If you suspect your teeth might be rotting, pay attention to these warning signs:
- Visible discoloration: Teeth may appear brown, black, or gray.
- Bad breath: Persistent foul breath often indicates the presence of decay.
- Pain: Sensitivity or severe pain while eating or drinking can signal issues.
- Swelling: Gums around the affected teeth may appear swollen or inflamed.
- Unpleasant taste: A lingering bad taste in the mouth can also be a warning sign.
How rotten teeth affect your body?
Having rotten teeth can greatly influence overall health status. Here are several ways this condition can affect you:
1. Increased Risk of Heart Disease.
Bacteria from decaying teeth can enter the bloodstream, leading to heart infections or heart disease. This connection underscores the importance of oral hygiene. Regular visits to the dentist can help prevent such severe issues.
2. Respiratory Issues.
When harmful bacteria from rotten teeth and gums are inhaled into the lungs, they can cause respiratory infections. This can be particularly dangerous for those with existing lung conditions.
3. Diabetes Complications.
If you have diabetes, poor dental health can exacerbate the disease. Infections in the mouth can affect blood sugar levels, making diabetes tougher to manage. Keeping your teeth healthy is vital for overall diabetes control.
4. Pregnancy Risks.
For expecting mothers, rotten teeth can pose risks to both their health and the baby’s health. Gum disease and tooth decay are linked to premature births and low birth weight. Proper dental care before and during pregnancy is critical.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies.
Rotten teeth can make eating painful, which might lead to a limited diet. This can result in nutritional deficiencies that affect your overall health. A well-rounded diet is important for maintaining energy and body function. If you can’t eat certain foods due to dental pain, you may miss essential vitamins and minerals.
Preventing tooth decay and its effects:
Taking preventive measures is the most effective way to avoid the complications associated with rotten teeth. Here are some strategies to keep your teeth and gums healthy:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
- Limit sugary snacks and beverages, which can contribute to decay.
- Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups.
- Drink plenty of water, especially fluoridated water, to aid oral health.
Preventive measures to avoid tooth decay:
Taking care of your teeth is essential for maintaining good oral health. To avoid tooth decay, there are several preventive measures you can adopt. By following these simple steps, you can protect your teeth from cavities and other dental issues.
Practice good oral hygiene:

Brush your teeth at least twice a day. Use fluoride toothpaste, which helps to strengthen tooth enamel and fight decay. Ensure you brush for a full two minutes. Don’t forget to brush your tongue too, as bacteria can accumulate there.
Floss every day to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth. This is an area where your toothbrush may not reach effectively. Regular flossing keeps your gums healthy and reduces the risk of cavities.
Limit sugar intake:
High sugar consumption is a leading cause of tooth decay. Bacteria in your mouth feed on sugar, producing acid that attacks your teeth. To reduce your risk:
- Choose healthier snacks like fruits, vegetables, and nuts instead of candy and sugary treats.
- Drink water instead of sugary drinks. If you consume soda or juice, do so in moderation and try to rinse your mouth with water afterward.
- Read labels and be mindful of hidden sugars in processed foods.
Stay hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water not only helps keep you hydrated but also wash away food particles and acids that can harm your teeth. Drinking water with fluoride can further strengthen your enamel and reduce the risk of decay.
Use dental products with fluoride:
Fluoride is a natural mineral that can help remineralize your teeth and prevent decay. Look for toothpaste and mouth rinse that contain fluoride. Some communities also fluoridate their water supply, which can help offer additional protection against cavities.
Avoid smoking and tobacco use:
Using tobacco products can greatly harm your oral health. Smoking leads to gum disease and increases your risk of tooth decay. Quitting smoking not only benefits your teeth but also your overall health.
Protect your teeth:
If you play sports or engage in physical activities, consider wearing a mouthguard. This device can help protect your teeth from injury and reduce the risk of fractures that can lead to decay.
Monitor acidic food and drinks:
Acidic foods and drinks can erode enamel, making your teeth more susceptible to decay. Limit your consumption of:
- Citrus fruits and juices.
- Soda and energy drinks.
- Wine and vinegar-based dressings.
If you do consume acidic foods or beverages, wait at least 30 minutes before brushing your teeth. This allows your enamel time to remineralize.
By integrating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can effectively reduce the likelihood of tooth decay. Taking care of your teeth ensures they remain strong and healthy for years to come. Remember, healthy teeth contribute to a healthy smile!
Professional dental treatment:
The most effective way to address rotten teeth is through professional dental treatment. Here are some common procedures:
- Fillings: For small cavities, a dentist will remove the decayed part of the tooth and fill it with materials like composite resin, amalgam, or gold. Fillings are effective in restoring function and appearance.
- Crowns: If a tooth is extensively decayed, a crown may be necessary. A crown covers the entire tooth, providing strength and protection. This is a durable solution, often lasting many years.
- Root Canals: When decay reaches the pulp of the tooth, a root canal may be needed. The dentist removes the infected pulp and seals the tooth. Although some fear this procedure, it is effective in saving the tooth and relieving pain.
- Extractions: In cases where the tooth is beyond repair, extraction may be necessary. While losing a tooth is not ideal, it can prevent further decay and infection.
At-Home treatments:
While professional help is essential for serious decay, certain at-home treatments can help improve oral health. However, it’s crucial to consult with a dentist before relying solely on these methods:
- Fluoride Toothpaste: Using toothpaste with fluoride can help strengthen your teeth and potentially reverse early signs of decay. Regular brushing is crucial for overall oral hygiene.
- Salt Water Rinse: A saltwater rinse can reduce inflammation and help soothe an aching tooth. This is a simple way to maintain oral health, though it does not treat decay.
- Oil Pulling: Some people find oil pulling with coconut oil can help remove bacteria and improve gum health. However, scientific evidence on its effectiveness for decay is limited.
Natural remedies:
While not a substitute for professional care, some natural remedies may alleviate symptoms or help prevent further decay:
- Clove Oil: Applying clove oil can act as a natural anesthetic and may help ease tooth pain due to its antibacterial properties.
- Garlic: Known for its antifungal and antibacterial properties, garlic may help fight bacteria associated with decay. Consider incorporating it into your diet for its potential benefits.
Conclusions:
Rotten teeth can have a significant impact on both your oral health and overall well-being. As you have learned, identifying the visual characteristics of rotten teeth is vital. Look for discoloration, dark spots, and visible decay. Understanding the causes behind tooth decay—like poor oral hygiene, sugary diets, and lack of regular dental check-ups—can empower you to make better choices for your teeth.
