The role of autoimmune diseases in causing tooth decay:
Autoimmune diseases can have far-reaching effects on your body, and one area that often goes overlooked is dental health. If you’re wondering how autoimmune diseases might lead to tooth decay, you’re not alone. Many people are unaware that their immune system, when confused by autoimmune conditions, can inadvertently contribute to various dental problems.
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells. This malfunction can create a number of complications, including those affecting oral health. Several autoimmune diseases are linked to higher rates of tooth decay. Below, we explore some of these conditions and their connection to dental issues.
Common autoimmune diseases linked to tooth decay:
Understanding which autoimmune diseases are associated with tooth decay is crucial. The following disorders have been known to adversely affect oral health:
- Sjögren’s Syndrome: This condition causes dry mouth (xerostomia) due to a decrease in saliva production. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids from food and bacteria. A lack of saliva leads to a higher risk of cavities and tooth decay.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inflammation in the body can lead to gum disease, which is often accompanied by tooth loss. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis may struggle to maintain proper oral hygiene, further increasing the risk of decay.
- Lupus: This chronic autoimmune disease can result in oral ulcers and dry mouth. Both these symptoms may contribute to a higher incidence of tooth decay.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: This condition may also lead to dry mouth and increased bacteria in the oral cavity, both of which make tooth decay more likely.
- Celiac Disease: Individuals with this condition may experience malabsorption of nutrients, which affects overall health, including that of their teeth. A deficiency in calcium and vitamin D can make teeth more vulnerable to decay.
How autoimmune diseases contribute to tooth decay?
Understanding the mechanisms behind tooth decay in autoimmune conditions can help in managing oral health effectively. Here are some contributing factors:
- Dry Mouth: As noted, reduced saliva due to autoimmune diseases plays a significant role in oral health. Saliva not only washes away food particles but also contains minerals that help protect teeth. Without it, your teeth become susceptible to decay.
- Gum Disease: Chronic inflammation and other factors associated with autoimmune diseases can lead to periodontal disease. This condition can cause gum recession, exposing tooth roots and leading to increased tooth decay.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Autoimmune diseases may interfere with nutrient absorption, which is vital for maintaining strong teeth. Conditions like celiac disease result in the ineffective uptake of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Pain and Discomfort: Many autoimmune diseases cause pain, making it difficult for individuals to maintain their dental care routines. If brushing and flossing create discomfort, dental hygiene may suffer, resulting in an increased risk of decay.
Managing oral health with autoimmune diseases:
If you suffer from an autoimmune disease, managing oral health becomes even more essential. Here are several strategies you can use:
- Stay Hydrated: Increasing water intake can assist in alleviating dry mouth. sugar-free gum or mints can also stimulate saliva production.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Frequent visits to your dentist can help in catching problems before they escalate. Your dentist can also provide tailored advice based on your specific condition.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily. Consider using a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid causing irritation, especially if you have sensitive gums.
- Healthy Diet: Ensure you’re getting a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support oral health. Discuss nutritional supplements with your healthcare provider if needed.
Understanding the connection between autoimmune diseases and tooth decay is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. By recognizing the risk factors and implementing proactive strategies, you can significantly improve your dental well-being, even in the face of an autoimmune challenge.
How Sjögren’s syndrome affects oral health?
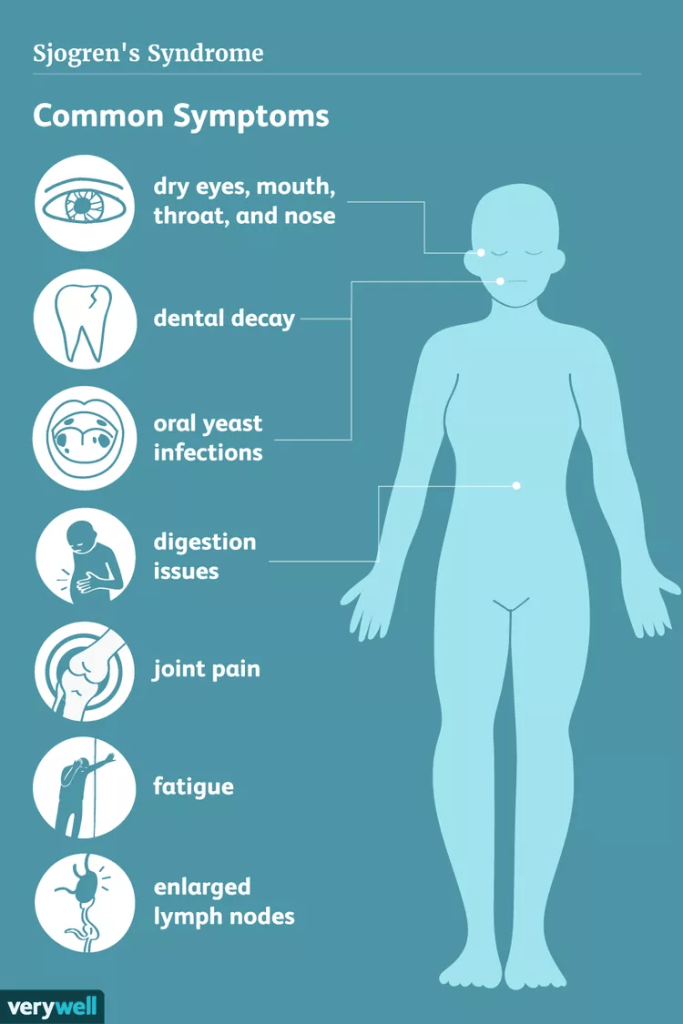
Sjögren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the body’s moisture-producing glands. One of the most significant impacts of this condition is on oral health. Understanding how Sjögren’s syndrome affects your mouth can help you find effective ways to manage your oral care.
Individuals with Sjögren’s syndrome often experience dry mouth, also known as xerostomia. This dryness occurs because the salivary glands are attacked by the immune system. Saliva is crucial for maintaining oral health, as it helps in washing away food particles, neutralizing acids produced by bacteria, and providing essential minerals to the teeth. When saliva production is reduced, several oral health issues can arise. Here are a few:
- Increased Tooth Decay: The lack of saliva creates an environment where harmful bacteria can thrive. This increases the likelihood of cavities and tooth decay.
- Gum Disease: A dry mouth can lead to swollen gums and gum disease. The balance of bacteria in the mouth is disturbed, making gums more susceptible to infection.
- Oral Infections: Without adequate saliva, the body’s defenses against bacteria are weakened, making infections more likely.
- Mouth Sores: People with Sjögren’s syndrome may experience frequent sores or ulcers in the mouth due to irritation and dryness.
Another common issue for individuals with Sjögren’s syndrome is dry throat. This can make swallowing uncomfortable and may also lead to hoarseness or voice changes. When the throat is dry, it can cause difficulty in eating and speaking, adding further complications to maintaining good oral hygiene.
Dry mouth and dry throat can also affect dental prosthetics. If you wear dentures or partials, you may find them uncomfortable or difficult to wear due to insufficient moisture. This discomfort can lead to reduced retention and an inclination to stop wearing them altogether.
Maintaining oral hygiene is crucial for anyone with Sjögren’s syndrome, but especially for those suffering from its symptoms. Here are some strategies to help manage oral health effectively:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. This can help alleviate dryness and keep the mouth moist.
- Use Saliva Substitutes: There are various over-the-counter saliva substitutes and mouth moisturizers that can provide relief for dry mouth.
- Mouth Rinses: Look for alcohol-free mouth rinses that can help with dryness without causing irritation.
- Chew Sugar-Free Gum: Chewing gum can stimulate saliva production and promote oral moisture.
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule regular check-ups to monitor your oral health. Your dentist can identify early signs of decay or gum disease.
Medication can also play a role in alleviating some of the symptoms associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications that encourage saliva production. Along with these treatments, staying informed about your condition can empower you to manage your oral health better.
People with Sjögren’s syndrome should also be mindful of their diet. Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can significantly benefit oral health. Foods that contain fluoride, calcium, and vitamin D can help strengthen teeth and reduce the risk of decay. Limiting sugary snacks and drinks is also crucial, as they can exacerbate tooth decay in those with a diminished saliva flow.
Sjögren’s syndrome poses significant challenges to oral health mainly through its effects on saliva production. By taking proactive steps—such as improving hydration, utilizing saliva substitutes, and maintaining regular dental check-ups—you can better manage the risks and improve your overall oral hygiene. If you have Sjögren’s syndrome, it’s essential to communicate openly with your dental care provider about your condition so you can work together to find the best approaches for maintaining your oral health.
The connection between Rheumatoid arthritis and dental issues:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune condition primarily known for its impact on joints. However, research has shown that this disease can also significantly affect dental health. If you have RA, you may want to pay attention to your oral health, as several factors link the two. Understanding this relationship can help you manage your condition and maintain a healthier smile.
One of the primary ways that rheumatoid arthritis can influence dental health is through dry mouth, or xerostomia. This condition occurs when the salivary glands don’t produce enough saliva. People with RA are often on medications such as corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that can inadvertently cause dry mouth.
Saliva plays a vital role in keeping your mouth healthy by washing away food particles and bacteria. When saliva levels drop, you become more susceptible to tooth decay and other dental problems.
Furthermore, individuals with RA may experience increased gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. The inflammation associated with RA can extend beyond the joints, affecting the gums and tissue surrounding the teeth. This inflammation can lead to swollen, bleeding gums, and an increased risk of tooth loss. Regular dental check-ups become essential for those with RA to monitor and manage these potential issues proactively.
Another factor to consider is the role of oral hygiene. People with rheumatoid arthritis may struggle to maintain proper oral care due to joint discomfort and stiffness, making it challenging to perform daily activities like brushing or flossing. It is crucial to find ways to adapt your oral care routine to ensure that you can still keep your teeth and gums healthy. Here are some tips:
- Utilize electric toothbrushes that require less effort.
- Consider using adaptive tools designed for individuals with limited dexterity.
- Schedule regular appointments with your dentist to monitor your dental health closely.
- Discuss any side effects of medications with your healthcare provider to find alternatives that don’t affect your oral health.
The connection between rheumatoid arthritis and dental issues can also be exacerbated by certain lifestyle factors. Smoking and poor dietary choices can worsen inflammation and increase your risk of gum disease and tooth decay.
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports immune function and overall health, helping to reduce these risks. Drinking plenty of water can also benefit your dental health by stimulating saliva production.
Interestingly, dental health can influence overall health as well, including the severity of arthritis symptoms. Studies have indicated that treating periodontal disease may lead to lower levels of inflammation, which could ease some RA symptoms.
The mouth is often considered a window to the body, and maintaining good oral health can potentially improve systemic conditions, including autoimmune diseases like RA. This connection underscores the importance of holistic health practices.
Moreover, if you notice changes in your gums or teeth, don’t ignore them. Swollen gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, or loose teeth are all signs that should prompt immediate dental consultation.
Early intervention can prevent more severe dental problems from arising. Your dentist can help create an individualized care plan that considers both your dental health and your arthritis management.
Understanding lupus and its impact on teeth:
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, and organs. One of the lesser-known consequences of lupus is its impact on oral health, including tooth decay. Understanding how lupus influences dental health is crucial for those diagnosed with the condition, as it allows individuals to take proactive measures to protect their teeth and gums.
When the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, it creates inflammation. This inflammation can also occur in the mouth, leading to various dental issues. Patients with lupus may experience dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, which can significantly affect oral health.
Saliva plays a vital role in protecting teeth; it helps neutralize acids produced by bacteria and wash away food particles. With reduced saliva flow, the risk of tooth decay increases.
Several factors contribute to tooth decay in lupus patients:
- Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva production can cause difficulty in swallowing and make it harder to maintain oral hygiene.
- Medication Side Effects: Many lupus treatments, including corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, can lead to dry mouth as a side effect.
- Gum Disease: Lupus can cause gingivitis or periodontitis, making gums more susceptible to infection and decay.
- Diet Changes: People with lupus may alter their diets due to symptoms, which can impact their nutritional intake and oral health.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is especially important for individuals diagnosed with lupus. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Regular Dental Visits: Schedule regular check-ups with your dentist to monitor your oral health. Inform your dentist about your lupus diagnosis to tailor your care accordingly.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help alleviate dry mouth symptoms. Consider sugar-free gum or candies to stimulate saliva production.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily. Use toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth if you experience discomfort.
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support overall health.
Additionally, it’s important to recognize the warning signs of potential dental issues. If you notice any of the following, consult your dentist promptly:
- Persistent bad breath
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Swelling or bleeding gums
- Loose teeth
- Unexplained pain in the mouth or teeth
Prevention strategies for tooth decay in autoimmune patients:
Tooth decay can pose significant challenges for individuals with autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune conditions, such as Sjögren’s syndrome and lupus, can lead to dry mouth and other oral health issues that increase the risk of cavities and gum disease. Understanding effective prevention strategies can help protect your teeth and ensure better overall oral health.
One crucial aspect of preventing tooth decay is maintaining proper oral hygiene. Regular brushing and flossing are vital, but the products you choose may impact your effectiveness. Here are some specific tips:
- Use Fluoride Toothpaste: Fluoride is known for its cavity-fighting properties. Automatic patients should opt for a fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel.
- Brush Twice Daily: Make sure to brush your teeth in the morning and before bed. This helps remove plaque and food particles that contribute to decay.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps reach areas that your toothbrush might miss. Ensure to floss gently to avoid irritating your gums.
- Mouthwash: Consider using an antibacterial mouthwash. This can reduce bacteria in your mouth and provide extra protection against cavities.
In addition to hygiene practices, hydration plays a key role in oral health, particularly for individuals with autoimmune diseases. A dry mouth can lead to an increase in bacteria, exacerbating the risk of tooth decay. Here are some hydration-focused strategies:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Stay hydrated throughout the day. Drinking water helps wash away food particles and neutralizes acids in your mouth.
- Chew Sugar-Free Gum: Chewing gum stimulates saliva production, which can help neutralize acids and protect your teeth. Look for products with xylitol, which is beneficial for dental health.
- Sip Water Frequently: Consider keeping water on hand to sip throughout the day, particularly if you experience dry mouth.
Diet also plays a significant role in preventing tooth decay. People with autoimmune diseases should be mindful of what they eat and how it affects their oral health. Here are some dietary strategies:
- Limit Sugary Foods: Sugar feeds harmful bacteria in your mouth, leading to decay. Try to limit sweets, sodas, and processed foods.
- Incorporate Calcium-Rich Foods: Foods like yogurt, cheese, and leafy greens are rich in calcium, which strengthens teeth and bones.
- Consume Whole Foods: Whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and lean proteins can enhance overall health and contribute to better oral health.
- Monitor Acidic Foods: Foods like citrus fruits can be acidic and may damage enamel. Enjoy them in moderation and rinse your mouth with water afterward.
By implementing these prevention strategies, individuals with autoimmune diseases can reduce their risk of tooth decay and maintain a healthy mouth. Consistent oral care, hydration, a balanced diet, regular dental visits, and effective management of autoimmune conditions are key steps towards achieving exceptional dental health.
Conclusions:
Understanding the relationship between autoimmune diseases and tooth decay is vital for those affected by these conditions. Autoimmune disorders like Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus significantly impact oral health. These conditions can reduce saliva production, create inflammation, and alter immune responses, all of which contribute to an increased risk of cavities and gum disease. It’s essential to recognize these risks early on.
However, there is hope. By implementing effective prevention strategies, individuals with autoimmune diseases can safeguard their dental health. This might include regular dental check-ups, staying hydrated to prevent dry mouth, using fluoride treatments, and maintaining a diligent oral hygiene routine.
Taking these steps is not just about preserving your teeth; it’s about ensuring a healthier, more comfortable future.
